|
Background: |
E1A-like inhibitor of differentiation-1 (EID-1), an acetyltransferase enzyme, binds both the retinoblastoma protein (Rb), a regulator of cell cycle and tissue specific transcription, and the adenovirus E1A-associated cellular p300 transcriptional co-activator protein. EID-1 inhibits cellular differentiation by blocking the histone acetyltransferase activity of p300. EID-1 also acetylates both histones and non-histone proteins such as NCOA3 co-activator. By acetylating histones, EID-1 gives a specific tag for transcriptional activation. In addition to binding Rb and p300, EID-1 also binds to phosphorylated CREB protein, mediating cAMP gene regulation. EID-1 augments the activity of phosphorylated CREB and activates transcription of cAMP responsive genes as a co-activator. |
|
Applications: |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
|
Name of antibody: |
EID1 |
|
Immunogen: |
Fusion protein of human EID1 |
|
Full name: |
EP300 interacting inhibitor of differentiation 1 |
|
Synonyms: |
CRI1; EID-1; RBP21; PTD014; C15orf3; PNAS-22; IRO45620 |
|
SwissProt: |
Q9Y6B2 |
|
ELISA Recommended dilution: |
1000-2000 |
|
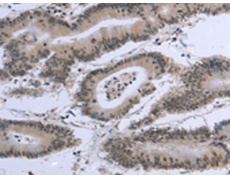
IHC positive control: |
Human colon cancer and human esophagus cancer |
|
IHC Recommend dilution: |
25-100 |
|
WB Predicted band size: |
21 kDa |
|
WB Positive control: |
Mouse heart tissue |
|
WB Recommended dilution: |
200-1000 |


 購(gòu)物車(chē)
購(gòu)物車(chē) 幫助
幫助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009