中文名稱:兔抗COX11多克隆抗體
|
Background: |
Cytochrome c oxidase (COX), the terminal component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, catalyzes the electron transfer from reduced cytochrome c to oxygen. This component is a heteromeric complex consisting of 3 catalytic subunits encoded by mitochondrial genes and multiple structural subunits encoded by nuclear genes. The mitochondrially-encoded subunits function in electron transfer, and the nuclear-encoded subunits may function in the regulation and assembly of the complex. This nuclear gene encodes a protein which is not a structural subunit, but may be a heme A biosynthetic enzyme involved in COX formation, according to the yeast mutant studies. However, the studies in Rhodobacter sphaeroides suggest that this gene is not required for heme A biosynthesis, but required for stable formation of the Cu(B) and magnesium centers of COX. This human protein is predicted to contain a transmembrane domain localized in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. A related pseudogene has been found on chromosome 6. |
|
Applications: |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
|
Name of antibody: |
COX11 |
|
Immunogen: |
Fusion protein of human COX11 |
|
Full name: |
cytochrome c oxidase copper chaperone COX11 |
|
Synonyms: |
COX11P |
|
SwissProt: |
Q9Y6N1 |
|
ELISA Recommended dilution: |
2000-10000 |
|
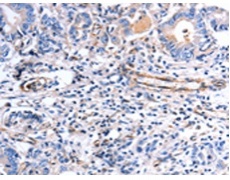
IHC positive control: |
Human stomach cancer |
|
IHC Recommend dilution: |
25-100 |
|
WB Predicted band size: |
31 kDa |
|
WB Positive control: |
Mouse brain tissue |
|
WB Recommended dilution: |
1000-5000 |


 購物車
購物車 幫助
幫助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009